Abstract
The major aim of this project is to visualize the data and to communicate the concepts behind the data clearly and efficiently to users. Stochastic Volatility Models are used in the field of mathematical finance to evaluate derivative securities. In this project, we choose the SABR model and the CIR model to investigate. The data set concludes the implied volatilities of interest rate swaption, natural gas price and electricity basis swap data from Bloomberg and ICAP. Then we use these data to estimate parameters in the SABR model and the CIR model. Finally, we apply the calibrated models to visualize the implied volatility surfaces. We also use it to visualize the swap curve.
Conclusions:
To sum up, we choose SABR model and CIR model to visualize the implied volatility surface of the ATM interest rate swaption, the swap curves of Natural Gas swap and Electricity swap. For the first part, the implied volatility surface we get is almost the same with what we downloaded from Bloomberg, which means the parameters we calculated are correct and the least-square method is perfect to estimate parameters. As for the second part, the basis swap curves we get match the data from ICAP well, and they have the same trend.
Researchers:
Research Group (2014 Fall):
Yi Zou, Master in Financial Engineering, Graduated in Jan 2015
Shiyu Wang, Master in Financial Engineering, Graduated in Jan 2015
Mengxi Wang, Master in Financial Engineering, Graduated in Jan 2015
Advisor:
Dr. Ionut Florescu
Research Topics:
The SABR Model, The CIR Model, Implied Volatility Surfaces, Swap Curve
Main Results:
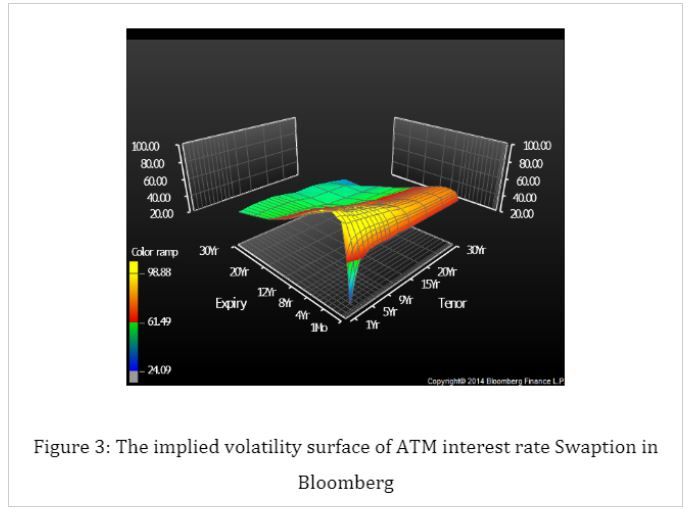
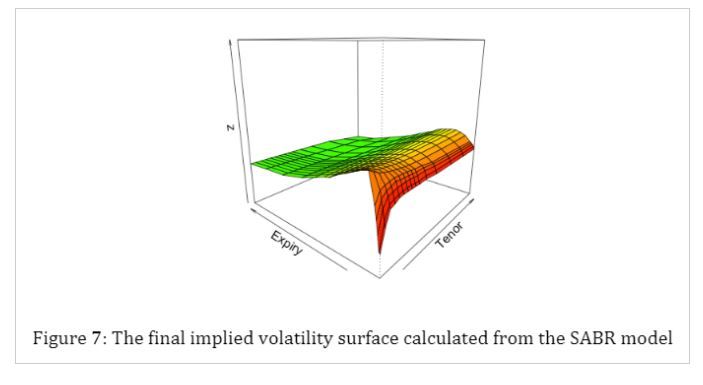
The two surfaces are almost the same except for some points with small expiry and tenor.
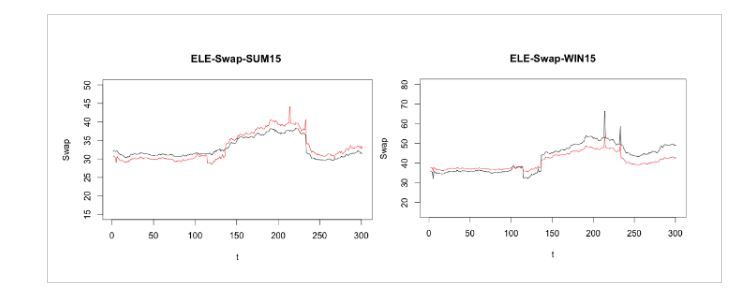
We can see the swap curves we get from the CIR model are very near from the swap curves from the market.